The data is in: 2024 is the year AI at work gets real. Use of generative AI has nearly doubled in the last six months,1 with 75% of global knowledge workers using it. And employees, struggling under the pace and volume of work, are bringing their own AI to work. While leaders agree AI is a business imperative, many believe their organization lacks a plan and vision to go from individual impact to applying AI to drive the bottom line. The pressure to show immediate ROI is making leaders inert, even in the face of AI inevitability.
We’ve come to the hard part of any tech disruption: moving past experimentation to business transformation. Just as we saw with the advent of the internet or the PC, business transformation comes with broad adoption. Organizations that apply AI to drive growth, manage costs, and deliver greater value to customers will pull ahead.
At the same time, the labor market is set to shift again—with AI playing a major role. Despite fears of job loss, leaders report a talent shortage for key roles. And as more employees eye a career move, managers say AI aptitude could rival experience. For many employees, AI will raise the bar but break the career ceiling.
To help leaders and organizations overcome AI inertia, Microsoft and LinkedIn looked at how AI will reshape work and the labor market broadly, surveying 31,000 people across 31 countries, identifying labor and hiring trends from LinkedIn, and analyzing trillions of Microsoft 365 productivity signals as well as research with Fortune 500 customers. The data points to insights every leader and professional needs to know—and actions they can take—when it comes to AI’s implications for work.
Already, AI is being woven into the workplace at an unexpected scale. 75% of knowledge workers use AI at work today, and 46% of users started using it less than six months ago. It’s paying off:
Users say AI helps them save time (90%), focus on their most important work (85%), be more creative (84%), and enjoy their work more (83%).
The heaviest Teams users (the top 5%) summarized 8 hours of meetings using Copilot in the month of March, the equivalent of an entire workday.2
“We’re at the forefront of integrating AI to not just work faster, but to work smarter. It’s our responsibility as organizational leaders to ensure that this technology elevates our teams’ creativity and aligns with our ethical values.”
While most leaders agree AI is a necessity, the pressure to show immediate ROI is making leaders move slowly.
79% of leaders agree their company needs to adopt AI to stay competitive, but 59% worry about quantifying the productivity gains of AI.
This uncertainty is stalling vision: 60% of leaders worry their organization’s leadership lacks a plan and vision to implement AI.
Three Out of Four People Use AI at Work
Usage nearly doubled in the last six months.
Doughnut-style chart shows 75% of people use AI at work, of which 46% only started using it less than six months ago.
Survey Questions:
How often do you use generative artificial intelligence (AI) for your work?
How long have you been using generative artificial intelligence (AI) at work?
Without guidance or clearance from the top, employees are taking things into their own hands and keeping AI use under wraps:
78% of AI users are bringing their own AI tools to work (BYOAI)—it’s even more common at small and medium-sized companies (80%).
And it’s not just Gen Z—BYOAI cuts across all generations.
52% of people who use AI at work are reluctant to admit to using it for their most important tasks.
53% of people who use AI at work worry that using it on important work tasks makes them look replaceable.
This approach means missing out on the benefits that come from strategic AI use at scale. It also puts company data at risk in an environment where leaders’ #1 concern for the year ahead is cybersecurity and data privacy.
BYOAI Is Not Just for Gen Z
Employees across every age group are bringing their own AI tools to work.

Survey Question:
Are the generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools you use at work provided by your organization?
Another driver of BYOAI: work has accelerated faster than employees’ ability to keep up.
68% of people say they struggle with the pace and volume of work, and 46% feel burned out.
Email overload persists—85% of emails are read in under 15 seconds, and the typical person has to read about 4 emails for every 1 they send.3
Meetings and after-hours work are holding steady at their post-pandemic highs, and the workday still skews toward communication: in the Microsoft 365 apps, users spend 60% of their time on emails, chats, and meetings, and only 40% in creation apps like Word and PowerPoint.4
“These findings align perfectly with how our brains manage the trade-offs between routine task execution and innovation—different kinds of thinking supported by two distinct but interacting neural networks in the brain. When we’re constantly switching, we don’t work as well. AI can help liberate workers from menial work and enable innovation and creativity to flourish.”
As AI use surges ahead, leaders who are “extremely familiar” with AI see its potential to be as transformational as the shift from a typewriter to a computer. Within the next five years, 41% of these leaders expect to redesign business processes from the ground up with AI. In the same time frame, they anticipate orchestrating (38%) and training a team of AI bots (42%), and ensuring the ethical use of AI (47%) will be a core part of their job.
The data is clear: People are overwhelmed with digital debt and under duress at work—and they are turning to AI for relief. The opportunity for every leader is to channel this momentum into ROI.
We also see AI beginning to impact the job market. While AI and job loss are top of mind for many, the data offers a more nuanced view—one with a hidden talent shortage, employees itching for a career change, and massive opportunity for those willing to skill up on AI.
Leaders are hiring: The majority (55%) of leaders say they’re concerned about having enough talent to fill roles in the year ahead. These leaders sit across functions, but the number jumps to 60% or higher for those in cybersecurity, engineering, and creative design.
Professionals are looking: While some professionals worry AI will replace their job (45%), about the same share (46%) say they’re considering quitting in the year ahead—higher than the 40% who said the same ahead of 2021’s Great Reshuffle. And in the US, LinkedIn studies show a 14% increase in job applications per role since last fall, with 85% of professionals considering a new job this year.5
The Hidden Talent Shortage
While employees fear job loss due to AI, most leaders worry they can’t fill key roles.

Survey Question:
When you think about your company in the year ahead, how much of a concern are each of the following?
Leaders have already made their landgrab for technical AI talent, with hiring up 323% in the past eight years. Now they’re turning their sights to non-technical talent with AI aptitude—the skills to use generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Copilot:
66% of leaders say they wouldn’t hire someone without AI skills.
71% say they’d rather hire a less experienced candidate with AI skills than a more experienced candidate without them.
And junior candidates may have a new edge: 77% of leaders say, with AI, early-in-career talent will be given greater responsibilities.
“Over the past few decades, companies have been renegotiating the psychological contract—the why of work—with their employees, influenced by new generations, labor trends, and the pandemic. Now companies must renegotiate the ‘operational contract’—the how of work—with their employees as AI puts more power into the hands of workers in terms of the way the job gets done.”
While leaders recognize the value of bringing on new employees with AI aptitude, they’re missing the value of developing their own people:
45% of US executives are not currently investing in AI tools or products for employees.6
Only 39% of people globally who use AI at work have gotten AI training from their company.
Only 25% of companies are planning to offer training on generative AI this year, further cementing this training deficit.7
The New Hiring Imperative
AI aptitude takes center stage.
Three donut-style charts showing that early-in-career talent will get greater responsibilities with AI (77%); that leaders are more likely to hire a less experienced candidate with AI skills than a more experienced one without them (71%); and that leaders would not hire someone without AI skills (66%).
Survey Questions:
To what extent do you agree or disagree with the following statements about generative artificial intelligence's (AI’s) impact on skills?
◦ I would be more likely to hire a less experienced candidate with AI skills than a more experienced candidate without AI skills
◦ In considering job candidates, I would not hire someone without AI skills
◦ Because they can delegate more work to AI, early-in-career talent will be given greater responsibilities
Professionals aren’t waiting for official guidance or training—they’re skilling up.
76% say they need AI skills to remain competitive in the job market.
69% of people say AI can help get them promoted faster, and even more (79%) say AI skills will broaden their job opportunities.
In the past six months, the use of LinkedIn Learning courses designed to build AI aptitude has spiked 160% among non-technical professionals, with roles like project managers, architects, and administrative assistants looking to skill up most.
We’ve also seen a 142x increase in LinkedIn members globally adding AI skills like ChatGPT and Copilot to their profiles—with writers, designers, and marketers topping the list. Marketers are interested for good reason. Two of the top ways B2B marketers say they plan to use generative AI this year include increasing efficiency to focus on higher value work (55%) and creating optimized and engaging content that resonates with target audiences (51%). When it comes to industries, surprisingly, administrative and support services, real estate, and retail lead the way—ahead of the tech industry.
For the vast majority of people, AI isn’t replacing their job but transforming it, and their next job might be a role that doesn’t exist yet:
Globally, skills are projected to change by 50% by 2030 (from 2016)—and generative AI is expected to accelerate this change to 68%.
More than two-thirds (68%) of this year’s LinkedIn’s Jobs on the Rise (fastest-growing roles in the US) didn’t exist 20 years ago.
12% of recruiters say they are already creating new roles tied specifically to the use of generative AI.
Head of AI is emerging as a new must-have leadership role—a job that tripled over the past five years and grew by more than 28% in 2023.
AI Aptitude Heats Up Across Roles and Industries
AI is going mainstream, and creative professionals are skilling up fast.
And just as we saw with flexible work options, offering AI access could help companies attract top talent:
LinkedIn job posts that mention artificial intelligence or generative AI have seen 17% greater application growth over the past two years compared to job posts that don’t mention them.
In another study, 54% of early-in-career and individual contributor employees—the future of the workforce—said that access to AI would influence their choice of employer.
In fact, 22% of recruiters already say they’re updating job descriptions to reflect the usage of generative AI in the role.
And future-looking organizations are already taking action. Many of LinkedIn’s Top Companies this year—including JPMorgan Chase, Procter & Gamble, and AT&T—are offering their teams AI learning opportunities to drive transformation at scale.
These are signs that AI could be a rising tide that elevates skills across roles and industries. Entry-level workers will take on more strategic projects, while uniquely human skills like management, relationship building, negotiation, and critical thinking will come to the fore for employees at all levels. Organizations that understand this will retain and attract the best talent, and professionals who skill up will have the edge.
In our research, four types of AI users emerged on a spectrum—from skeptics who rarely use AI to power users who use it extensively, with novices and explorers in between. When we studied the difference between skeptics and power users we saw notable gaps, not only between how they work but how they feel about work.
The Power User Payoff of AI at Work
Power users are reshaping the workday and reaping the benefits.
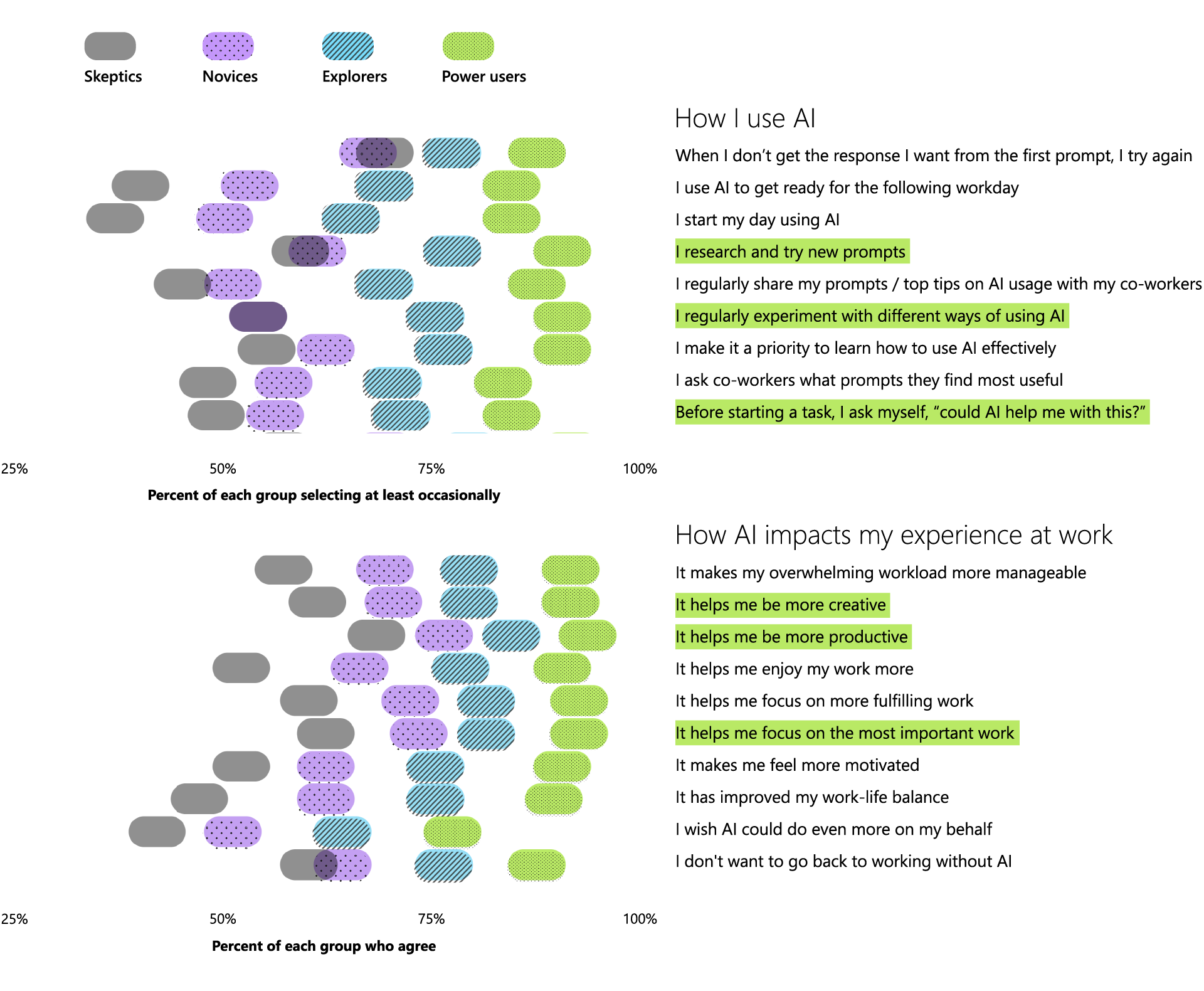
Skeptics are at least familiar with AI, but they only use it a few times a month (if ever). They say AI saves them 10 minutes or less per day. Novices are only somewhat familiar with AI (if at all) and use it only a few times a month (if ever). They say AI saves them 30 minutes or less per day. Explorers are only somewhat familiar with AI (if at all) and use it a few times a month or once a week. They say AI saves them between 5 and 30 minutes per day. Power Users are at least familiar with AI and use it at least several times per week. They say it saves them more than 30 minutes per day.
_________________
Survey Questions:
When using artificial intelligence (AI) at work, how frequently do you do each of the following?
We’d now like you to reflect on how you feel about using artificial intelligence (AI) in your work. To what extent do you agree or disagree with the following statements?
Power users are familiar to extremely familiar with AI, using it at work at least several times a week and saving more than 30 minutes a day. And it’s paying off: power users say AI makes their overwhelming workload more manageable (92%), boosts their creativity (92%), and helps them focus on the most important work (93%)—and it helps them feel more motivated (91%) and enjoy work more (91%).
The path to becoming a power user starts with developing new habits. Power users are 68% more likely to frequently experiment with different ways of using AI—in fact, it’s the #1 predictor of whether someone will be a power user or not. When compared to other survey respondents, they’re also more likely to frequently pause before a task and ask themselves if AI can help (+49%), to keep trying if they don’t get the perfect response the first time (+30%), and to research and try new prompts (+56%). Power users also bookend their day with AI—using it to start the day (85%) and get ready for the following workday (85%).
Power users have also reoriented their work patterns in fundamental ways. They are 56% more likely to use AI to catch up on missed meetings, to analyze information (+51%), to design visual content (+49%), to interact with customers (+49%), and to brainstorm or problem-solve (+37%). And they’re already moving past individual tasks: they’re 66% more likely to redesign their business processes and workflows with AI.
The research also shows that power users are empowered by a different kind of organization. At their companies:
Senior leaders lean in: AI power users are 61% more likely to hear from their CEO about the importance of using generative AI at work, 40% more likely to hear from the leader of their department, and 42% more likely to hear from their manager’s manager.
Company culture is change-ready: AI power users are 53% more likely to receive encouragement from leadership to consider how AI can transform their function and 18% more likely to say their company encourages innovation.
They get tailored training: AI power users are 37% more likely to say their company has a virtual learning program. They’re also more likely to have received training on prompt writing (+37%), how to use AI for their role or function (+35%), or specific use cases such as writing or analyzing data (+32%).
“To stay ahead of the curve, we’ve made AI training a priority to ensure everyone can leverage the power of Microsoft 365 Copilot and other AI solutions. We also launched the GenAI Academy, supporting employee growth and development with the aim of increasing ambassadors and GenAI power users across the globe. We are already seeing benefits that are transforming the way we work and innovate.”
AI power users provide a window into the future—revealing what’s possible when employees embrace new ways of working and leaders lean in.
The opportunity ahead for leaders is to channel employee enthusiasm for AI into business transformation. This will look different for every organization, but here’s how to get started.
Identify a business problem, then apply AI: There are efficiency gains to be had across every function—the key is to pick a process and apply AI. For example, start with customer service and focus on improving call-handling time. Global advertising network dentsu applied AI to its creative development process. Estée Lauder is using it to reimagine product development and customer experience.
Take a top-down, bottom-up approach: Going from experimentation to transformation requires engagement at every level of the organization, from the CEO to the entry-level employee. Business gains will come when you enlist your business line leaders to activate teams around AI. As we’ve rolled out Copilot at Microsoft, we’ve relied on internal champions at all levels to model and spread AI enthusiasm and aptitude.
Prioritize training: AI power users aren’t doing it on their own—they receive ongoing training, both on universal tasks and uses more tailored to their role and function. LinkedIn Learning is a great place to start to skill up, and the Copilot Scenario Library provides use cases for specific roles and functions.
We’ve arrived at a pivotal moment for AI at work. Just as we look back at the pre-PC era, we’ll one day wonder how work got done without AI. Already, AI is helping people be more creative and productive, and giving job seekers an edge. Over time, it will change every aspect of work. As we reach the hard part of this tech disruption—turning experimentation into tangible business impact—companies that face the challenge head-on will surge ahead. In this moment, fortune favors the bold.
See how the data compares for small and medium-sized businesses and in US metropolitan areas. Learn how Microsoft and LinkedIn are innovating to help organizations and professionals thrive in the era of AI.
1 46% of survey respondents who use generative AI at work have used it for less than six months.
2 Data represents intentional user Copilot query for meeting summarizations by commercial customers in a rolling 28-day period ending in March 2024. It does not include activity from Teams Intelligent Recap. Heaviest users represent the top 5% of users by number of Copilot queries. Excludes EU usage and education segment.
3 Data represents intentional email usage by commercial customers in a rolling 28-day period ending in March 2024. Excludes EU usage and education segment.
4 Collaboration patterns in Microsoft 365 in a rolling 28-day period ending in March 2024, excluding weekends. Time spent is represented by intentional activity in Microsoft 365 applications including Outlook, Teams, Word, PowerPoint, Excel, and OneNote. Intentional actions include things like attending a meeting, writing an email, analyzing data, and reviewing or editing a document. Includes commercial users and excludes education segment.
5 Research was conducted by Censuswide on behalf of LinkedIn among 1,013 US working professionals between November 24 and December 12, 2023.
6 Unpublished data from LinkedIn’s Executive Confidence Index
7 Unpublished data from LinkedIn’s 2024 Workplace Learning Report
Methodology
Work Trend Index Survey
The Work Trend Index survey was conducted by an independent research firm, Edelman Data & Intelligence, among 31,000 full-time employed or self-employed knowledge workers across 31 markets between February 15, 2024 and March 28, 2024. This survey was 20 minutes in length and conducted online, in either the English language or translated into a local language across markets. One thousand full-time workers were surveyed in each market, and global results have been aggregated across all responses to provide an average. In the US, an additional sample of 2,800 full-time employed or self-employed knowledge workers was collected across nine sub-regions/metros.
Global markets surveyed include:
Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, Colombia, Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Philippines, Poland, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, United Kingdom, United States, and Vietnam.
Sub-regions/Metros in the United States surveyed include:
Atlanta, Austin, Boston, DC Metro, Houston, New York City, North Carolina, Pittsburgh, and the San Francisco Bay Area.
Audiences mentioned in the report are defined as follows:
Knowledge Workers: those who typically work at a desk (whether in an office or at home). This group includes those who are in person or working remotely in some capacity.
AI Power Users: knowledge workers who are at least familiar with generative AI, use it at work at least several times a week, and save more than 30 minutes a day by using it.
Business Leaders/Business Decision Makers: knowledge workers in mid to upper job levels (i.e., SVP, VP, Sr. Director, General Manager, EVP, C-Suite, President, etc.) and have at least some decision-making influence related to hiring, budgeting, employee benefits, internal communications, operations, etc.
Employees/Non-Business Decision Makers: knowledge workers who are not in mid to upper job levels or have no influence on decision making related to hiring, budgeting, employee benefits, internal communications, operations, etc.
LinkedIn Economic Graph Research Institute
LinkedIn’s Economic Graph is a digital representation of the global workforce, covering over 1 billion members, 67 million companies, and 134,000 schools. LinkedIn’s Economic Graph Research Institute (EGRI) drives research focused on answering members’ and leaders’ top questions about the economy and the labor market, based on the Economic Graph data. EGRI’s metrics in this report include*:
AI Aptitude Skills: These are standardized skills referring to the ability to use generative AI tools such as ChatGPT, Copilot, GitHub Copilot, etc.
Professionals adding AI Aptitude Skills: We compute the growth in the share of members adding AI Aptitude skills to their profiles, relative to the number of members adding any skill.
Top Occupations adding AI Aptitude Skills: For every occupation in the LinkedIn taxonomy, we compute the growth in the share of members adding AI Aptitude skills to their profiles, relative to the number of members adding any skill.
Head of AI Roles: We identify members whose job titles include the keywords “AI,” “Artificial Intelligence,” or “Machine Learning” coupled with the keyword “Head,” or LinkedIn’s standardized seniority levels “Director,” “VP,” and “CXO.” We then build a time series of the number of companies with at least one member in Head of AI roles.
LinkedIn’s Jobs on the Rise (JOTR) that didn’t exist 20 years ago (US only): Every year, we publish LinkedIn’s JOTR, a ranked list of the fastest growing jobs (in terms of number of members holding that title) over the previous three years. Internships, volunteer positions, interim roles, or student roles are excluded. To compute the share of JOTR that did not exist 20 years ago, we compared the list to O*NET’s 2000 taxonomy by name or job description. O*NET is the US primary source for occupational information, consisting of a database developed under the sponsorship of the US Department of Labor. It contains hundreds of job definitions and is used extensively in academic research.
Projected Skills Change: We predict how skills will change over time by looking at how they changed in the past and estimating how they will change in the future via linear extrapolation. We also consider the impact of generative artificiaI intelligence (GAI) technology by imagining a scenario where skills that can be easily replicated by GAI become less important compared to other important skills.
* Unless otherwise specified, results reported are global, including the UK, Germany, France, India, Singapore, Australia, and Brazil.
LinkedIn Executive Confidence Index
LinkedIn’s Executive Confidence Index (ECI) is an online survey taken every quarter by ~5,000 LinkedIn members (at the VP level or above). The most recent wave ran from March 4–19, 2024. Members are randomly sampled and must be opted into research to participate. We analyze data in aggregate and will always respect member privacy. Data is weighted by Seniority and Industry to ensure fair representation of executives on the platform. The results represent the world as seen through the lens of LinkedIn’s membership; variances between LinkedIn’s membership and the overall market population are not accounted for.
LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report
The LinkedIn Learning 2024 Workplace Learning Report surveyed 1,636 L&D and HR professionals with L&D responsibilities who have some influence on budget decisions, and 1,063 learners. Surveyed geographies include: North America (United States, Canada); South America (Brazil); Asia-Pacific (Australia, New Zealand, India, Japan, Cambodia, Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Thailand, Hong Kong); and Europe (United Kingdom, Ireland, Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg, Norway, Finland, Sweden, Iceland, Denmark, France, Germany, Austria).
2024 Global Marketing Jobs Outlook Report
Insights were leveraged from Ipsos & LinkedIn research conducted in 2023 using a sample of 1,577 senior-level B2B marketing leaders, including 377 CFOs, from various industries in NAMER (US), EMEA (UK, DE, FR) , APAC (IN, AU, SG), and LATAM (Brazil).